Proof of concept
Peer Approved article about MuTaTo by Dr Morad & Dr Itzhaki
"In this paper, we present MuTaTo©, a new personalized medicine concept for curing cancer patients. In the development of this concept, we have tried to address all of the factors that cause poor success rate in cancer treatment. We have designed experiments, that would show that the principles behind MuTaTo are sustainable."AEBi Article in Pharmafile May 2019 (Pharmafocus.com)
In May 2019 PharmaFile (www.magazine.pharmafile.com) published an article by Dr Morad and Dr Itzhaki about AEBi work.
Link to a PDF Link https://adobe.ly/2L0JspQ
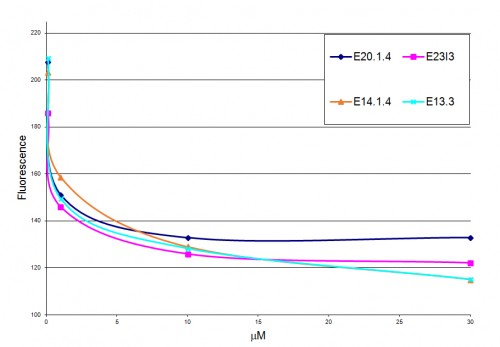
The effect of several peptides on the phosphorylation levels of human EGFR in A431 cell line was assessed by ELISA test: Exponentially growing A431 cells were seeded on a 96-well plate, and grown for about 3 days. Following medium exchange, solutions containing 50 mg/ml EGF and 0.2 mg/ml peptides were added. The plate was incubated for 7.5 min at 37 ºC. The medium was removed, the cells fixed, and the plate washed with Triton washing solution. The level of phosphorylates was assessed by incubation with phospho-EGFR (Tyr1045) antibody as a primary antibody, and Anti-rabbit IgG as a secondary antibody. The ability of different peptides to inhibit autophosphorylation of EGFR is presented by the decrease of the fluorescent signal (Y axis).
Accumulation of Fluorescent PEG-Peptide In Mice’s Cancer Tumors
EGFR antagonist peptide, attached to PEG, was labeled with Fluorescein, and injected intravenously to 5 Xenograft mice, bearing subcutaneous NCI-H1650 tumors (lung cancer that overexpress EGFR). The 6th mouse served as time 0, and was injected only with saline. Each mouse was subjected to anesthesia, perfusion and organ collection at a specific time point. The organs were homogenized in a volume of solution proportional to their weight, and spun down. Fluorescence of each sample was measured.
As can be seen, our peptide reached its targeted tumor cells, and accumulated there, unlike in the kidneys and the liver, where its concentration went down again.
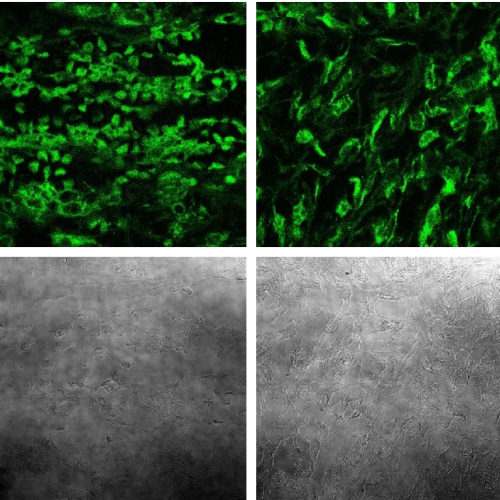
Internalization of Fluorescent PEG-Peptide into Cancer Cells in Mice’s Tumors
The upper part of the photograph shows fluorescently labeled cancer cells taken from the tumors 1 hour and 24 hours after the injection. The lower part is a regular photograph of the same cells (no excitation that causes the fluorescence emission). In this part, cells that did not interact with the fluorescent peptide may be seen, but it looks like all, or most of the cells interacted with, and internalized the fluorescent peptide.
Efficacy Test - Killing Cancer Cells
We have synthesized a molecule that contains several copies of EGFR targeting peptide, which are bound to several copies of two different toxic peptides. We have tested the effect of this molecule on two kinds of cancer cell lines:
- A431 – Human epithelial carcinoma that contains around 100,000 copies of EGFR on each cell.
- MCF-7- Breast adenocarcinoma that contains around 3,000 copies of EGFR on each cell (a partial negative control).
- Solutions were applied to the cells in a 96 well plate, and after 48 hours the wells were photographed.
Results
As can be seen in the photographs, at concentrations above 3 micromolar, all A431 cells lost their tissue-like structure, and died. The partial negative control - survived.
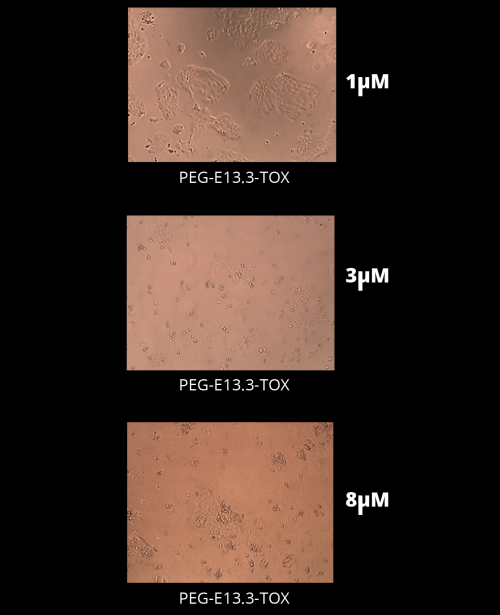

Partial negative control

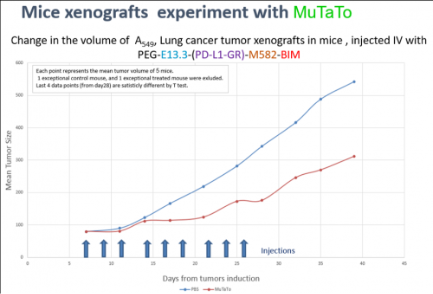
Mice experiment was performed by HBI Biotech Sciences (former Envigo https://www.inotivco.com/) . In this experiment we induced xenograft tumors of A549 (Human lung cancer) in 12 mice.
Only after the tumors were established (solid tumors) six mice were treated with MuTaTo.
That MuTaTo contained for the first time three different targeting peptides and one kind of a toxic peptide.
The other six mice served as a control group. They were treated with saline.
We gave 3 IV injections per week, for three weeks, and continue following the tumors for another week.
It is important to emphasize that the MuTaTo was injected to the tail vein of the mice not to the Tumor.
The results showed that the tumors development was inhibited in the test group, comparing to the control group.
Even after we stopped injections the tumors did not regain their accelerated rate of development.
AEBI LTD. ANNOUNCES THAT THE UNITED STATES PATENT OFFICE HAS ISSUED A PATENT FOR ITS DRUG DISCOVERY PLATFORM
TEL AVIV, ISRAEL – (December , 2018) – AEBI Ltd. (“AEBI” or the “Company”), a preclinical-stage biopharmaceutical company developing novel lead molecules for the treatment of certain types of cancer and many other diseases, today announced that the United States Patent and Trademark Office (USPTO) will issue a patent for the Company’s drug discovery platform technology. US Patent No. 10,160,967 entitled Methods and Compositions for Identifying a Peptide Having an Intermolecular Interaction With a Target of Interest is due to issue on December 25, 2018.
“This important patent in the United States augments the robust intellectual property position we are building globally. AEBI has been granted patents and has filed pending applications in major markets including the U.S and European Patent Office. We continue to strengthen our intellectual property portfolio through new patent filings on the most recent inventions, including peptide molecules identified by use of AEBI’s proprietary platform technology,” stated Dan Aridor, Chairman of the Board of AEBI. “The US is one of the largest markets in the world for development of peptide drug molecules, especially designed to provide solutions for diseases with few effective treatment options available. We look forward to developing peptide-based drug leads as a potential treatment to serve these unmet needs.”
About AEBI’s Drug discovery platform
AEBI’s Drug Discovery technology provides a method for identifying peptide molecules which have an interaction with a target of interest. Simply stated, AEBI’s technology can identify new molecules that should be able to increase a desired interaction or to diminish or prevent an undesired interaction. Sometimes the peptides themselves may serve as potential drugs or they may serve as a basis for improved drug designs.
This invention provides a recombinant bacteriophage virus libraries, wherein each virus contains a protein involved in viral attachment or infection, a polypeptide which differs by at least a single amino acid from another peptide or polypeptide in the library, and a modified cleavage site that is proximal to the peptide and the protein. The cleavage site is modified such that a compound mediating cleavage has a reduced binding affinity for it as compared to a non-modified cleavage site. The invention further involves a “target of interest complex” comprising a protease, a target of interest involved in an intermolecular interaction, and a flexible linker that attaches the protease and target of interest. This complex technology provides a method for identifying a peptide which has an interaction with a target of interest or identifying the agonistic or antagonistic feature of a peptide that has an intermolecular reaction with a target of interest.
About AEBI
AEBi, Based in Nes-Ziona, Israel is a development-stage biopharmaceutical company engaged in the discovery and development of therapeutic peptides, was established in the year 2000 in a technology incubator at Weizmann Science Park, Israel. The company believes that the ability to discover novel therapeutic peptides has vastly superior advantages to many existing and trajectory technologies of drug development.
6th Drug Discovery Innovation Programme - AEBI-Bio Press release.
The 6th Drug Discovery Innovation Programme is all set to highlight the recent advances in research techniques for the Discovery and Designing of new drugs.
This Conference will bring together research scientists, medicinal chemists, CSOs, CEOs and educational institutions under one roof from all over Europe to discuss the latest scientific advances in the field of drug discovery & development that help to face current and future challenges in discovery research.
Dr. Ilan Morad, CEO, AEBi will be the Keynote Speaker at 6th DDIP on 29-30 November 2018 at Leonardo Hotel Frankfurt City – South & he will be imparting insights on AEBi recent results on its proof of concept for a revolutionary Complete Cure for Cancer.
AEBi solution is based on AEBi’s combinatorial drug discovery platform. Dr. Morad will discuss the advantages of AEBI solution both a generic and personal medicine. Recent trends are providing additional support to Dr Morad claim that a simultaneous coordinated attack on cancer cells based on the same structure- carrier via overexpressed receptors is the way to go.
WorldBi Group provides business executives with tailored practical conferences, topical seminars, and in-house training programs, keeping them up-to-date with industry trends, technological developments, and the regulatory landscape.
The conference will feature opening and closing plenary keynote sessions, pre-conference workshop, interactive breakout discussion groups, and networking. It is an opportunity for leaders from large, mid-sized, and small pharma, biotech, vendor companies, and academic research centers to come together to share best practices and discuss the new era of AI-driven precision medicine.
More information about this event can be found at https://worldbigroup.com/confere…/sixth-drug-discovery/index

Following previous lectures in 2017 Dr. Morad was asked to present again in front of peers in the prestigious www.worldbi.com conference of Drug Discovery Innovation Program (DDIP#6). The conference was held on the 29th of November 2018.
Promo to Dr Morad lecture by WorldBI



Dr Ilan Morad founder and CEO of www.AEBI-bio.com Delivering the opening presentation of the Drug Discovery IP 4 conference in Boston, USA. Titled – A Complete Cure for Cancer!